47 results found

The value of private investment in PPP infrastructure has gradually declined over the past decade.



Globally, foreign equity in private infrastructure deals amounted to around 12% of total private infrastructure investment over the past decade, with Sub-Saharan Africa having a particularly high reliance on foreign equity.



Sustainable low-carbon private investments have intensified in high-income countries. To strengthen global response to combat climate change, such investments must be accelerated in developing countries.



Private infrastructure investment in low-income countries is almost entirely denominated in foreign currencies, implying a structural foreign exchange risk for investors.



Over the past decade, about three-quarters of private infrastructure investment globally was debt financed, and about a quarter was equity financed.



Infrastructure equities have an attractive risk-return profile providing a competitive alternative to other investment options.


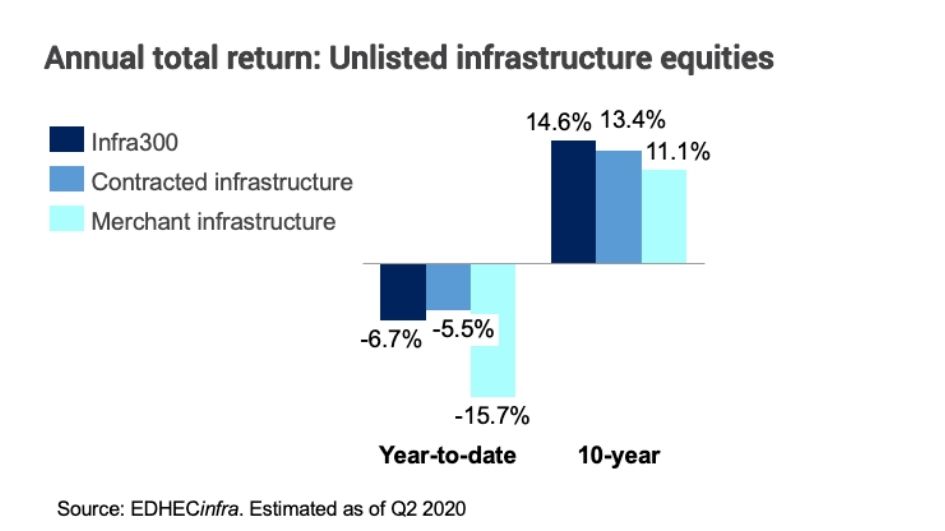
Merchant infrastructure, larger investors and the transport sector have experienced larger declines in returns due to COVID-19.



Infrastructure equities have an attractive risk-return profile providing a competitive alternative to other investment options.



Merchant infrastructure, larger investors and the transport sector have experienced larger declines in returns due to COVID-19.


Electricity investment and ICT adoption seem to be positively correlated. There is probably some degree of causation.

Countries that have lower levels of total infrastructure investment per capita are more likely to experience higher air pollution rates.

Mortality rates attributed to household and ambient air pollution are strongly negatively correlated to total infrastructure investment per capita.








