
 Back
Back
Data Insights
Discover data-driven insights on selected infrastructure themes that have been developed from multiple sources to analyse infrastructure investment flows and their performance, providing momentum to strengthen data-driven discussions and decisions.
12 results found

On average, around 40% of the primary infrastructure transactions that involve private sector participation also involve a public institution. However, this varies by income group.


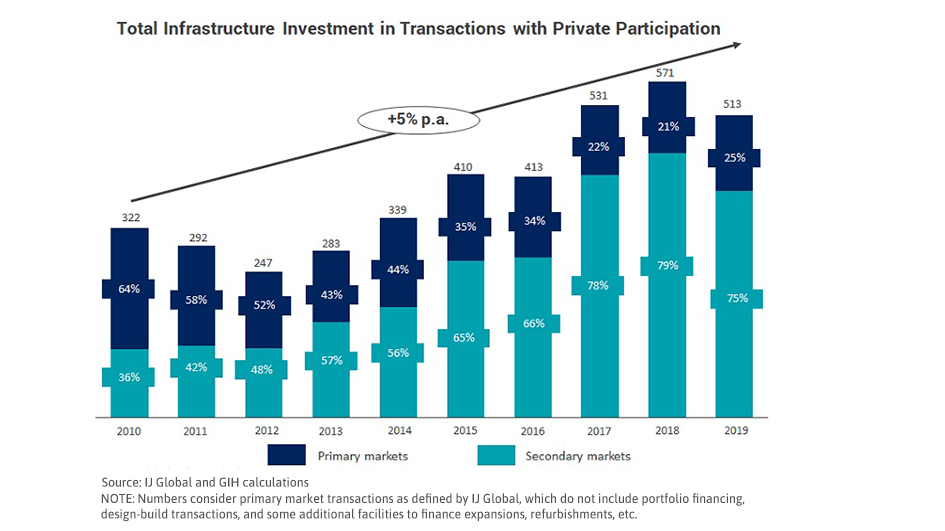
While total infrastructure investment with private participation has increased over the past decade, this has been driven by secondary market transactions. Primary market transactions are low and have been declining.



Private investment in social infrastructure has seen a sharp decline over the past decade, driven by the healthcare and social housing sub-sectors. In the transport sector, around half of private investment over the past decade has been in the roads, tunnels and bridges sub-sector.



Europe has seen the largest number of infrastructure transactions with private participation over the past decade, although the average value of these transactions tends to be relatively small compared with other regions.



The value of private investment in PPP infrastructure has gradually declined over the past decade.



Globally, foreign equity in private infrastructure deals amounted to around 12% of total private infrastructure investment over the past decade, with Sub-Saharan Africa having a particularly high reliance on foreign equity.



Sustainable low-carbon private investments have intensified in high-income countries. To strengthen global response to combat climate change, such investments must be accelerated in developing countries.



Private infrastructure investment in low-income countries is almost entirely denominated in foreign currencies, implying a structural foreign exchange risk for investors.



Over the past decade, about three-quarters of private infrastructure investment globally was debt financed, and about a quarter was equity financed.



Over the past decade, global private investment into infrastructure has amounted to around USD 100-150 billion annually, excluding secondary market transactions.



In 2019, renewables attracted the largest amount of private investment among infrastructure sectors, followed by transport and non-renewable power. Renewables accounted for 40% of total private infrastructure investment in 2019. Meanwhile, private investment in social infrastructure (healthcare, education and public facilities) has declined over the past decade from USD 19 billion in 2010 to USD 3 billion in 2019.



Private infrastructure investment is dominated by high-income countries. In 2019, more than 80% of global private infrastructure investment was in high-income countries, with particularly strong investment in the renewables sector. High-income countries attract more than triple the amount of capital invested in middle- and low-income countries.


